Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimada, Taro; Nishimura, Yuki; Takeda, Seiji
MRS Advances (Internet), 2(12), p.687 - 692, 2017/01
A disposal measure for fuel debris generated at the accident in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station has been studied so far. However, physical and chemical properties of the fuel debris have not yet investigated in reactor containment vessels. In order to investigate the safety function of barriers required for disposal of fuel debris, sensitivity analyses for radionuclide migration were carried out, considering with uncertainty of the properties. As a result, it is indicated that it was important for evaluation of fuel debris disposal to obtain the physical and chemical properties of  C and
C and  I during release to groundwater, in addition to
I during release to groundwater, in addition to  U.
U.
Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji; Mukai, Masayuki; Munakata, Masahiro; Tanaka, Tadao
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1744, p.229 - 234, 2015/04
Integrated safety assessment methodology which analyzes radionuclide migration reflecting the spatial and temporal changes of disposal systems was developed for a geological disposal site with uplift and denudation, and then some case analyses for an assumed site with sedimentary rocks were carried out. The combination of uniform uplift and denudation has the most effect on the radionuclide migration because the groundwater flow velocity increases with decreasing the depth from the ground surface. In the case without denudation, tilted uplift has more effect than uniform uplift because flow velocity in tilted uplift increase with increasing hydraulic gradient. The long-term change of the geological structures including the uplift and denudation, the hydraulic conditions, and the recharge and outlet of the groundwater around a candidate site should be carefully investigated to determine the appropriate the place,depth and layout of the repository.
Miyahara, Kaname; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.245 - 256, 2013/10
After the Fukushima Dai-ichi accident, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was chosen by the Government to conduct decontamination model projects at selected sites. Despite tight boundary conditions in terms of timescale and resources, the decontamination model projects provide a good basis for developing recommendations on how to assure clean-up efficiency and reduce time, cost, subsequent waste management and environmental impact. This can be summarised in terms of site characterisation and data interpretation, clean-up and waste minimisation and storage.
 (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH

Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Kitamura, Akira
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.231 - 236, 2013/10
For the nuclear waste management of TRU waste, it is necessary to assess the impact of nitrate salts contained in the waste. In the present study, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was investigated in the presence of NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 . Under different NH
. Under different NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 concentration, pH and ionic strength conditions, distribution coefficient (
concentration, pH and ionic strength conditions, distribution coefficient ( ) of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was determined by batch experiment. For Ni system, the
) of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was determined by batch experiment. For Ni system, the  values showed no significant dependence on the initial NH
values showed no significant dependence on the initial NH
 concentration in neutral pH region, agrees with the prediction from thermodynamic data. For Pd system, the
concentration in neutral pH region, agrees with the prediction from thermodynamic data. For Pd system, the  values decreased with an increase of [NH
values decreased with an increase of [NH
 ]ini, suggesting the formation of stable ammine complex (Pd(NH
]ini, suggesting the formation of stable ammine complex (Pd(NH )
)
 (
( : 1 - 4)). The obtained
: 1 - 4)). The obtained  values for Ni and Pd were analyzed using the surface complexation model. By taking complexes predicted by thermodynamic data into account, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd in the presence of NH
values for Ni and Pd were analyzed using the surface complexation model. By taking complexes predicted by thermodynamic data into account, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd in the presence of NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 were well explained.
were well explained.
Takeda, Seiji; Inoue, Yoshihisa; Kimura, Hideo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.237 - 242, 2013/10
The sensitive analysis of radionuclide migration for the scenarios on deterioration or loss of safety functions expected in HLW disposal system due to the human error (initial defective scenarios) is performed in this study. Release rates for Cs-135 and Se-79 are estimated from Monte Carlo-based analysis. Maximum release rates of radionuclides for initial defective scenarios, buffer (colloidal transport case) and sealing plugs (pathway of short-circuit), are about one or two order magnitude higher than that normal scenario. From a viewpoint of future safety review, these results especially indicate the need to understand the feasibility on two types of initial defective scenario for the buffer and sealing plugs, leading to the loss of restraint of colloidal migration in the buffer and the loss of restraint with the plugs from migration through dominant pathway in tunnels and their vicinity.
Sasaki, Toshiki; Kaminishi, Shuji*; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Funasaka, Hideyuki
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.257 - 268, 2013/10
The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident and restoration works have produced significant volume of radioactive waste. The waste has very different characteristics from usual radioactive waste produced in nuclear power stations and it requires extensive research and development for management of the waste. R&D works such as radionuclide analysis of the waste, hydrogen generation/diffusion analysis of a storage vessel, corrosion evaluation of storage vessels, etc. have been performed for characterization and safe storage of the waste. The detailed R&D plan for processing and disposal waste will be established by the end of FY2012.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.269 - 275, 2013/10
Following the release of radionuclides into the environment as a result of the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) had to develop an immediate and effective method of reducing the dose rate received by students in school facilities. A demonstration of a reducing method was carried out by JAEA at a junior high school ground and kindergarten yard in the center of Fukushima-city. Dose rates of the released radionuclides are largely controlled by the ground level contamination and accumulation of mainly cesium-137 ( Cs) and cesium-134 (
Cs) and cesium-134 ( Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5
Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5  Sv/h to 0.15
Sv/h to 0.15  Sv/h.
Sv/h.
Sato, Haruo; Niizato, Tadafumi; Amano, Kenji; Tanaka, Shingo; Aoki, Kazuhiro
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.277 - 282, 2013/10
The accident of the TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant occurred by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on 11 March, 2011. It is estimated that 1.2-1.5 10
10 Bq for
Bq for  Cs and 1.5-1.6
Cs and 1.5-1.6 10
10 Bq for I-131 were released until the beginning of April and those radionuclides (RN) were deposited on soil surface and forest etc. widely around Fukushima Pref. This work was carried out as one of the investigations for making the distribution maps of radiation dose rate and soil contaminated by RNs which the MEXT promotes. The Geoslicer investigation on the depth distribution of RNs in soil was carried out after 3 months from the accident. The investigation was conducted at 11 locations in Nihonmatsu City, Kawamata Town and Namie Town, and soil samples of depth 50 cm to 1 m were taken. Both of
Bq for I-131 were released until the beginning of April and those radionuclides (RN) were deposited on soil surface and forest etc. widely around Fukushima Pref. This work was carried out as one of the investigations for making the distribution maps of radiation dose rate and soil contaminated by RNs which the MEXT promotes. The Geoslicer investigation on the depth distribution of RNs in soil was carried out after 3 months from the accident. The investigation was conducted at 11 locations in Nihonmatsu City, Kawamata Town and Namie Town, and soil samples of depth 50 cm to 1 m were taken. Both of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were detected in all investigated locations, and
Cs were detected in all investigated locations, and 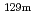 Te and
Te and 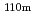 Ag were detected only in areas where radiation dose rates are high. At many locations investigated, radiocaesium more than 99% distributed within a depth of 10 cm in soil in the surface layer. On the other hand, RNs tended to distribute to deeper part in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer, and radiocaesium more than 99% in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland also distributed within a depth of around 14 cm. The apparent diffusion coefficients of RNs derived from penetration profiles near the surface layer showed a tendency to be higher in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer. The distribution coefficients by a batch method were also obtained for Cs and I, and the relationship between D
Ag were detected only in areas where radiation dose rates are high. At many locations investigated, radiocaesium more than 99% distributed within a depth of 10 cm in soil in the surface layer. On the other hand, RNs tended to distribute to deeper part in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer, and radiocaesium more than 99% in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland also distributed within a depth of around 14 cm. The apparent diffusion coefficients of RNs derived from penetration profiles near the surface layer showed a tendency to be higher in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer. The distribution coefficients by a batch method were also obtained for Cs and I, and the relationship between D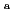 and K
and K was discussed.
was discussed.
Harjo, S.; Tsuchida, Noriyuki*; Gong, W.; Abe, Jun; Aizawa, Kazuya
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1528 (Internet), 7 Pages, 2013/01
Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) is one of important effects of steel strengthening mechanism to improve strength, ductility and excellent high-speed deformation behavior. To measure strengthening mechanism of TRIP steel during deformation, in situ neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation was performed. Two kinds of TRIP steels with different carbon content were prepared. Neutron diffraction measurements were performed using beamline 19 TAKUMI, a pulsed-neutron TOF diffractometer in J-PARC. Detail results will be shown and discussed during presentation.
 and zircalloy-2
and zircalloy-2Kato, Masato; Uchida, Teppei; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.91 - 96, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and zircalloy-2
and zircalloy-2Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Uchida, Teppei; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.97 - 101, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Komeno, Akira; Kato, Masato; Hirooka, Shun; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.85 - 89, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.165 - 168, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In  -wave unconventional superconductors, superconducting Cooper pairs are believed to be formed via magnetic fluctuations. In fact, superconducting transition temperature
-wave unconventional superconductors, superconducting Cooper pairs are believed to be formed via magnetic fluctuations. In fact, superconducting transition temperature 
 roughly correlates with antiferromagnetic spin fluctuation energy in
roughly correlates with antiferromagnetic spin fluctuation energy in  -wave unconventional superconductors including high
-wave unconventional superconductors including high 
 cuprates. In addition to this correlation, the superconducting pairing symmetry and the magnetic anisotropy of the normal state are found empirically to be strongly correlated in
cuprates. In addition to this correlation, the superconducting pairing symmetry and the magnetic anisotropy of the normal state are found empirically to be strongly correlated in  -electron unconventional superconductors having crystallographic symmetry lower than cubic. In antiferromagnetic systems, unconventional superconductivity appears with singlet (
-electron unconventional superconductors having crystallographic symmetry lower than cubic. In antiferromagnetic systems, unconventional superconductivity appears with singlet ( -wave) pairing for cases of XY anisotropy. In contrast, in ferromagnetic systems, unconventional superconductivity with triplet (e.g.
-wave) pairing for cases of XY anisotropy. In contrast, in ferromagnetic systems, unconventional superconductivity with triplet (e.g.  -wave) pairing appears for cases of Ising anisotropy. In this report, the origin of XY anisotropy is discussed in terms of the angler momentum character
-wave) pairing appears for cases of Ising anisotropy. In this report, the origin of XY anisotropy is discussed in terms of the angler momentum character 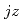 for each Fermi surfaces.
for each Fermi surfaces.
Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Osaka, Masahiko; Miwa, Shuhei; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Ito, Akinori; Homma, Yoshiya*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.149 - 158, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Besides the importance of AnO series (An; U, Np, Pu, Am) as a nuclear fuel, the magnetic properties of these compounds at low temperatures are particularly interesting. Their surprisingly varied physical properties continue to be of interest for both theory and experiment. In this study, we have performed NMR studies for the series of actinide dioxides. On the basis of
series (An; U, Np, Pu, Am) as a nuclear fuel, the magnetic properties of these compounds at low temperatures are particularly interesting. Their surprisingly varied physical properties continue to be of interest for both theory and experiment. In this study, we have performed NMR studies for the series of actinide dioxides. On the basis of  O-NMR studies, exotic magnetic orderings associated with multipole degrees of freedom on 5
O-NMR studies, exotic magnetic orderings associated with multipole degrees of freedom on 5 electrons have been identified in UO
electrons have been identified in UO (dipolar + quadrupolar ordering) and NpO
(dipolar + quadrupolar ordering) and NpO (octupolar + quadrupolar ordering), in contrast with the non-magnetic ground state of PuO
(octupolar + quadrupolar ordering), in contrast with the non-magnetic ground state of PuO . In AmO
. In AmO , our
, our  O-NMR data provide the first microscopic evidence for a phase transition as a bulk property in this system.
O-NMR data provide the first microscopic evidence for a phase transition as a bulk property in this system.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1298, 6 Pages, 2011/04
Dislocation channeling observed in irradiated metals is generated as the result of strain localization and it has been thought to be the dominant stress factor in irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking. In the present study, a hierarchical computational modeling based on atomistic and continuum simulations were constructed to describe the fundamental characteristics of the plastic deformation in irradiated materials. Several anomalous defects are introduced under irradiation. At first individual influences of the irradiation defects on plastic deformation can be identified by atomistic simulations. Then local interaction events between glide dislocation and irradiation defects were introduced into the crystal plasticity finite element analysis. We found that softening after the first yield event observed in experimental study is caused by annihilation of irradiation defects resulting from unfaulting by dislocation sweeping.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1298, p.61 - 66, 2011/04
The irradiation behaviour in two different precipitation hardening types of Ni-base alloys with the ultra high purity grade (EHP), namely, the  ' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe
' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe or Ni
or Ni ) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni
) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni , 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP(
, 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP( ') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along
') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along 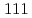 planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP(
planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP( '), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP(
'), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP( '), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
'), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
Lee, S.; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Matsui, Toshiya*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1265, p.209 - 214, 2010/11
A corrosion experiment were performed for carbon steel contacted with iron reducing bacteria. After incubation for 41 days, biofilm and some corrosion products were observed and determined by SEM analysis. It is clear that Vivianite, which is considered as a protect material for iron corrosion, has been generated as an iron corrosion product with contribution of iron reducing bacteria from this experiment.
Sugita, Yutaka; Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Aizawa, Takao*; Ito, Shunichiro*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1265, p.39 - 44, 2010/11
The creation of an excavation disturbed zone (EDZ) is expected around the gallery when the gallery is excavated in the underground to dispose the radioactive waste. In-situ EDZ experiment has been performed to determine the rock properties and width of the EDZ in 140m gallery at a depth of 140m below the surface at Horonobe URL. In the experiment, seismic tomography measurement was performed by using seismic source to observe width of the EDZ. Observation area is 3m square horizontal plane along the sidewall of the 140m gallery. During excavation of the 140m gallery, seismic tomography measurement was performed repeatedly with processing of excavation of the gallery, and the change of velocity distribution of the rock around the gallery was observed. Seismic tomography investigation caught the EDZ developed around the excavated gallery.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsuru, Tomohito; Shibutani, Yoji*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1215, 6 Pages, 2010/10
In the present study three types of grain boundaries of coincidence site lattice (CSL), small angle (SA), and random types are considered as the representative example of grain boundaries. The grain boundary energies and atomic configurations of CSL are first evaluated by first-principle density functional theory (DFT) and the embedded atom method (EAM) calculations. SA and random grain boundaries are subsequently constructed by the same EAM and the fundamental characteristics are investigated by the discrete dislocation mechanics models and the Voronoi polyhedral computational geometric method. As the result, it is found that stress distributions of CSL and SA grain boundaries are localized around the grain boundary core. The random grain boundary shows extremely heterogeneous core structures including a lot of pentagon-shaped Voronoi polyhedral resulting from the amorphous-like structure.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Osaka, Masahiko; Kurosaki, Ken*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Uno, Masayoshi*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1215, p.95 - 100, 2010/10
In order to investigate the effect of MAs and FP addition on the oxygen potential of MOX fuels, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) were carried out. MOX fuels with Am and 26 kinds of fission product elements (FPs), simulating low-decontamination MOX fuel and high burn-up to 250 GWd/t, were prepared by a conventional powder metallurgical route in a glove box. The oxygen potentials for simulating low-decontamination MOX fuels were higher than the fuels without FPs and increased positively with increasing simulated burn-up.